Journal of Clinical and Investigative Dermatology
Download PDF
No side effects were reported during the study, supporting the formula’s safety and tolerability.
Altogether, the objective findings align with the self-assessed improvements, supporting a concordance between perceived and measurable outcomes following two months of supplementation.
Research Article
Evaluation of a Grape Extract and Coenzyme Q10-Based Nutricosmetic Formula on Cellulite-Related Parameters
Emmanuelle Arnaud, Ilona Gille, Maïté Jeanroy, Benoit Lemaire and David Gaudout
Activ’Inside, Beychac-et-Caillau, France
*Address for Correspondence: Emmanuelle Arnaud, Activ’Inside, Beychac-et-Caillau, France,
Email: e.arnaud@activinside.com
Submission:28 November, 2025
Accepted:18 December, 2025
Published:20 December, 2025
Copyright: © 2025 Arnaud E, et al. This is an open access article
distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License,
which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in
any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Keywords: Nutricosmetic; Cellulite; Long-term efficacy; Grape extract;
Coenzyme Q10
Abstract
Background: Cellulite is a common cosmetic concern in women,
associated with alterations in microcirculation, adipocyte hypertrophy,
and connective tissue remodeling. Nutricosmetic formulations based
on natural extracts may represent a non-invasive option to support
long-term skin appearance.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of a patented oral formulation (Celluvine™) containing grape extract and coenzyme Q10 on celluliterelated parameters in women under real-world conditions.
Methods: This real-world study included women aged 30-50 years with a body mass index between 25 and 30 and visible cellulite. Participants consumed one capsule per day (283 mg) for two months, followed by a one-month follow-up without supplementation. Selfassessed parameters (orange peel appearance, water retention, physical complexes, self-confidence, body well-being, sensation of lightness) were rated on a 0-10 scale at baseline, 1 month, 2 months, and after follow-up. Objective measurements (weight, body fat, body circumferences) were performed at baseline and 2 months.
Results: Forty participants completed the protocol. After two months, significant improvements were reported in orange peel appearance (-22%), water retention (-25%), and physical complexes (-22%). Self-confidence (+56%), body well-being (+61%), and sensation of lightness (+98%) increased in parallel. Objective measures confirmed reductions in body weight (mean -2.3 kg), body fat (mean -12.4%), and waist (-5.9 cm), hips (-4.9 cm), and thighs (-4.4 cm) circumference. No adverse effects were reported. Benefits were maintained after the follow-up period.
Conclusions: Daily intake of the formulation was safe, well tolerated, and associated with measurable improvements in celluliterelated parameters and well-being. Larger placebo-controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings.
Objectives: To evaluate the effects of a patented oral formulation (Celluvine™) containing grape extract and coenzyme Q10 on celluliterelated parameters in women under real-world conditions.
Methods: This real-world study included women aged 30-50 years with a body mass index between 25 and 30 and visible cellulite. Participants consumed one capsule per day (283 mg) for two months, followed by a one-month follow-up without supplementation. Selfassessed parameters (orange peel appearance, water retention, physical complexes, self-confidence, body well-being, sensation of lightness) were rated on a 0-10 scale at baseline, 1 month, 2 months, and after follow-up. Objective measurements (weight, body fat, body circumferences) were performed at baseline and 2 months.
Results: Forty participants completed the protocol. After two months, significant improvements were reported in orange peel appearance (-22%), water retention (-25%), and physical complexes (-22%). Self-confidence (+56%), body well-being (+61%), and sensation of lightness (+98%) increased in parallel. Objective measures confirmed reductions in body weight (mean -2.3 kg), body fat (mean -12.4%), and waist (-5.9 cm), hips (-4.9 cm), and thighs (-4.4 cm) circumference. No adverse effects were reported. Benefits were maintained after the follow-up period.
Conclusions: Daily intake of the formulation was safe, well tolerated, and associated with measurable improvements in celluliterelated parameters and well-being. Larger placebo-controlled trials are needed to confirm these findings.
List of abbreviations
BMI: Body Mass Index; FMD: Flow-Mediated Dilation; NO:
Nitric Oxide; UHPLC-DAD: Ultra-High Performance Liquid
Chromatography coupled with Diode Array Detection; WHO: World
Health Organization
Introduction
Cellulite is a widespread cosmetic concern, affecting 80 to 98% of
post-pubescent women, compared to just 2% of men. This disparity
is due to differences in connective tissue structure: in women, the
fibers are organized in parallel, whereas in men they are arranged in
a crisscross pattern to provide greater resistance to the phenomenon.
The presence of cellulite is also influenced by hormonal factors and the distribution of fat, both of which play a crucial role in body weight [1,2]. In a context where rates of overweight and obesity continue to rise, this trend does not seem likely to reverse. Among women, the prevalence of being overweight increased from 19% in 1990 to 26% in 2022, while the prevalence of obesity doubled over the same period to reach 18% [3]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 43% of adults aged 18 and over were overweight in 2022, including 16% who were obese.
The presence of cellulite is also influenced by hormonal factors and the distribution of fat, both of which play a crucial role in body weight [1,2]. In a context where rates of overweight and obesity continue to rise, this trend does not seem likely to reverse. Among women, the prevalence of being overweight increased from 19% in 1990 to 26% in 2022, while the prevalence of obesity doubled over the same period to reach 18% [3]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), 43% of adults aged 18 and over were overweight in 2022, including 16% who were obese.
In 2023, 24% of consumers on diets in Europe used nutritional
supplements to support weight loss, demonstrating a growing
awareness of these issues and a proactive approach to addressing
them [4,5].
Cellulite is a cosmetic change to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, producing a dimpled or “orange-peel” appearance. There are three types of cellulite that can coexist:
• Aqueous cellulite, linked to water retention, is caused by poor blood and lymphatic circulation, leading to inadequate waste elimination, which causes tissue swelling and visible skin deformation. It often manifests as a feeling of heaviness in the legs and is visible without pinching the skin.
• Adipose cellulite, linked to fat deposits, results from an increase in the size and number of fat cells, which disrupts local circulation. This contributes to the skin’s visible deformation, characterized by an irregular appearance and loss of smoothness. It is often visible when pinching the skin.
• Fibrous cellulite is older and more ingrained. It results from the hardening of collagen fibers around fat cells, particularly due to glycation. This rigidity creates tension that pulls the skin downwards, resulting in the dimpled appearance characteristic of cellulite [6].
Cellulite is a cosmetic change to the skin and subcutaneous tissue, producing a dimpled or “orange-peel” appearance. There are three types of cellulite that can coexist:
• Aqueous cellulite, linked to water retention, is caused by poor blood and lymphatic circulation, leading to inadequate waste elimination, which causes tissue swelling and visible skin deformation. It often manifests as a feeling of heaviness in the legs and is visible without pinching the skin.
• Adipose cellulite, linked to fat deposits, results from an increase in the size and number of fat cells, which disrupts local circulation. This contributes to the skin’s visible deformation, characterized by an irregular appearance and loss of smoothness. It is often visible when pinching the skin.
• Fibrous cellulite is older and more ingrained. It results from the hardening of collagen fibers around fat cells, particularly due to glycation. This rigidity creates tension that pulls the skin downwards, resulting in the dimpled appearance characteristic of cellulite [6].
Despite its prevalence, current anti-cellulite solutions remain
largely topical or invasive, including creams, radiofrequency, and
cryolipolysis. These methods often provide transient or localized
results, without addressing the deeper physiological mechanisms
underlying cellulite formation. Consequently, there is a growing need
for innovative and more attractive, evidence-based nutricosmetic
strategies capable of acting from within, an alternative offering
durable benefits.
In this context, natural active ingredients such as green tea and
grape polyphenols, collagen and, coenzyme Q10 have attracted
increasing scientific and consumer interest. These compounds
are known to act on key biological pathways involved in cellulite
development, including microcirculation, adipocyte metabolism,
collagen synthesis, and oxidative stress, making them promising
candidates for oral formulations targeting skin firmness and texture.
To address these multifactorial mechanisms, Activ’Inside has
developed a patented nutricosmetic formula (Celluvine™). Its main
ingredients, grape extract and coenzyme Q10, are scientifically
validated and recognized active ingredients. The formula has
been specifically designed to target microvascular function, lipid
metabolism and collagen synthesis and protection.
Grape extract is rich in polyphenols, such as epicatechin and
ε-viniferin, which play a key role in improving microcirculation. In
vitro, ε-viniferin stimulates nitric oxide (NO) production, thereby
enhancing vasodilation [7,8]. Clinically, 200 mg of grape extract has
been shown to significantly improve flow-mediated dilation (FMD)
within two hours of ingestion, confirming its rapid effect on blood
flow [9]. Grape extract also affects fat metabolism, with in vivo studies
showing that it reduces adipocyte hypertrophy induced by a highfat
diet. Grape also increases GLUT4 expression in muscle, therefore
improving glucose uptake and reducing its storage in the form of fats
[10,11]. Grape’s strong antioxidant properties further support these
effects by reducing oxidative stress, protecting micro vessels and
preventing extracellular matrix degradation, all of which are involved
in the development of cellulite [12]. Grape extract therefore helps to
preserve skin structure from degrading collagen and elastin, helping
to maintain firm and elastic skin [13].
Coenzyme Q10 is a documented ingredient known for its ability
to stimulate natural collagen synthesis. In vitro studies show that it
significantly increases the expression of collagen types I, IV, and VII,
and enhances fibroblast proliferation. This supports dermal structure,
improving skin firmness and elasticity [14]. In a clinical study, daily
supplementation with 50 mg of coenzyme Q10 improved the texture
and appearance of the skin of healthy women, reducing the visible
signs of cellulite, such as an uneven surface and a lack of elasticity
[15]. In addition to its structural role, coenzyme Q10 offers antioxidant
protection by helping to neutralize reactive oxygen species (ROS),
which contribute to collagen breakdown and microvascular damage,
two factors that exacerbate cellulite [16].
The objective of this article is to investigate the potential
physiological effects of the combined oral intake of grape polyphenols
and coenzyme Q10 in the context of cellulite management. These two
bioactive ingredients are suggested to contribute to microcirculation,
adipocyte metabolism, and dermal structure maintenance.
Previous mechanistic studies indicate that grape polyphenols
may promote nitric oxide-dependent vasodilation, limit adipocyte
hypertrophy, and help preserve the extracellular matrix, while
coenzyme Q10 may contribute to collagen synthesis. Based on this
scientific rationale, we examined the relevance of these pathways
under real-world conditions using both subjective and objective
assessments of cellulite-related parameters.
Through this approach, the study aims to provide preliminary
evidence supporting the safety and mechanistic contribution of
grape extract and coenzyme Q10, which are the key bioactive
components of the patented nutricosmetic formulation Celluvine™.
These ingredients act through several complementary pathways,
including the improvement of microcirculation and antioxidant
activity. They also help maintain skin viscoelasticity, firmness, and
microrelief. Together, these effects contribute to visible and longterm
improvements in skin quality and overall well-being.
Materials and Methods
I. Product under investigation:
The product under investigation is a patented, proprietary
oral formulation containing grape extract, rich in monomers
and ε-viniferin, with coenzyme Q10 (Celluvine™, Activ’Inside,
France, patent FR3114497). Celluvine™ is standardized in flavanol
monomers (catechins and epicatechins) ≥ 10.6%, and total viniferins
(including ε-viniferin) ≥ 15 ppm using ultra-high performance liquid
chromatography coupled with diode array detection (UHPLCDAD).
This patented combination is characterized by specific levels
of ε-viniferin and flavanol monomers, two phenolic compounds
naturally found in grapes, whose synergistic action contributes to
the improvement or maintenance of endothelial function [17]. The
product was packaged as hard-shell capsules in bottles with a plain
white label.II. Real-world study – Design and participants:
This real-world study was conducted on 40 healthy French
women. The main inclusion criteria were being aged between 30 and
50 (mean age 43), having cellulite and/or water retention, a body
mass index (BMI) between 25 and 30 kg/m², and having consented to
participate in the study. Women who were pregnant or breastfeeding,
perimenopausal or menopausal, suffering from chronic illnesses,
taking oral or topical slimming/anti-cellulite treatments, or other
treatments likely to alter the appearance of their skin were not
eligible, nor were those who had made significant lifestyle changes
(diet or physical activity) in the 12 months preceding the study.
Participants were asked not to change their dietary or exercise habits
for the duration of the study (3 months). Throughout the threemonth
duration of the study, participants were specifically instructed
to maintain their usual dietary patterns and physical activity routines.
This meant that they were asked not to introduce any significant
changes to the types or quantities of foods they consumed, nor to
alter the frequency, intensity, or type of exercise they regularly
performed. The purpose of this instruction was to minimize potential
confounding factors, ensuring that any observed effects could be
more confidently attributed to the intervention being studied, rather
than to changes in diet or physical activity.They received one daily capsule containing 283 mg of the
nutricosmetic formula, to be taken with breakfast and a glass of water
for two months. An additional one-month follow-up phase without
supplement intake was added to assess the persistence of the effects
after stopping the supplementation. Compliance was verified at the
end of the supplementation.
To obtain consumers’ feedback, various parameters were
self-assessed by women, including orange peel appearance, water
retention, physical complexes, self-confidence, physical well-being,
and the sensation of lightness. These parameters were evaluated using
a self-administered numerical rating scale ranging from 0 (“not at all”
/ “none”) to 10 (“a lot” / “very high”). Assessments were performed
at baseline (T0), after one month (T1) and two months (T2) of
supplementation, and at the end of a one-month follow-up period
(T3) without supplementation.
At the same time, the effectiveness of the supplementation was
objectively evaluated by an anthropometric assessor. Weight (using a
weighing scale), body fat (using a body fat caliper), and circumference
of waist, hips, thighs, calves, arms, back/chest, and buttocks (using a
measuring tape) were objectively measured at the beginning of the
study and after two months of supplementation, as they are relevant
indicators of cellulite.
Statistical analyses were performed using the Student’s t-test for
paired samples, with results expressed as mean and a significance
threshold of p < 0.05.
Results
I. Compliance & safety:
The nutricosmetic formula was well tolerated during the 2-month
supplementation program. At the end of the study, participants
answered the question “During the last 60 days, have you forgotten
or have you not been able to take the product?”, to which 100% of
the women replied that they had followed the protocol completely,
without missing a single dose. In addition, 98% of women declared
that the supplementation was easy to follow.No side effects were reported during the study, supporting the formula’s safety and tolerability.
II. Self-assessment of cellulite-related parameters:
Participants rated six subjective parameters: orange peel
appearance, water retention, physical complexes, self-confidence,
body well-being, and sensation of lightness, on a 0-to-10 selfrating
scale at baseline (T0), after one (T1) and two (T2) months of
supplementation, and following a one-month observation period
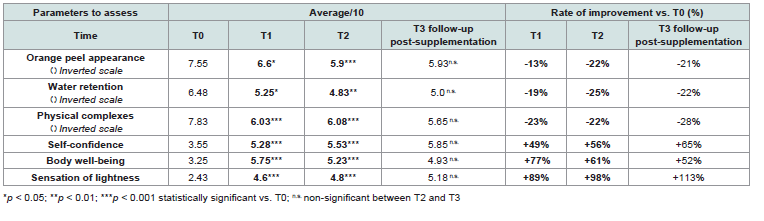
without supplementation (T3).The average scores obtained at each time point and their
percentage changes versus baseline are presented in [Table 1].
At baseline, participants reported a marked perception of discomfort related to cellulite. Mean scores for initial data for negative parameters such as orange-peel appearance, water retention, and body-image concerns ranged from 6.5 to 7.8 out of 10, indicating a moderate-to-high level of dissatisfaction.
At baseline, participants reported a marked perception of discomfort related to cellulite. Mean scores for initial data for negative parameters such as orange-peel appearance, water retention, and body-image concerns ranged from 6.5 to 7.8 out of 10, indicating a moderate-to-high level of dissatisfaction.
After one month of supplementation (T1), all three parameters
showed a statistically significant decrease (p < 0.05), which continued
throughout the supplementation, reaching values between 4.8 to 6.1
at the end, reflecting a perceived improvement. After two months of
supplementation, the mean percentage changes from baseline were
-22% for orange-peel appearance, -25% for water retention, and -22%
for physical complexes (p < 0.01), suggesting a visible improvement
in perceived skin texture and comfort.
Meanwhile, parameters related to well-being and self-perception, for which lower scores reflect greater discomfort, such as selfconfidence, body well-being, and sensation of lightness, increased progressively over time. Baseline scores for these parameters were relatively modest, ranged from 2.4 to 3.6, reflecting reduced selfperceived well-being. After two months, these scores dropped significantly, reaching values between 4.8 and 6.1, reflecting a perceived improvement. At the end, the average improvements reached +56% for self-confidence, +61% for body well-being, and +98% for sensation of lightness (p < 0.001).
These results highlight that the formulation was associated with significant improvements in reducing the appearance of cellulite and improving the psychological aspects related to it. One month after stopping supplementation (T3), scores remained stable across all domains, with no significant difference compared to T2, indicating a persistence of perceived benefits after the supplementation period.
Meanwhile, parameters related to well-being and self-perception, for which lower scores reflect greater discomfort, such as selfconfidence, body well-being, and sensation of lightness, increased progressively over time. Baseline scores for these parameters were relatively modest, ranged from 2.4 to 3.6, reflecting reduced selfperceived well-being. After two months, these scores dropped significantly, reaching values between 4.8 and 6.1, reflecting a perceived improvement. At the end, the average improvements reached +56% for self-confidence, +61% for body well-being, and +98% for sensation of lightness (p < 0.001).
These results highlight that the formulation was associated with significant improvements in reducing the appearance of cellulite and improving the psychological aspects related to it. One month after stopping supplementation (T3), scores remained stable across all domains, with no significant difference compared to T2, indicating a persistence of perceived benefits after the supplementation period.
III. Objective measurements of cellulite-related parameters:
Objective assessments were conducted to complement the selfreported
data. Anthropometric parameters, including body weight,
body fat percentage, and body circumferences (waist, hips, thighs,
arms, calves, back/chest, buttocks) were measured at baseline (T0)
and after two months of supplementation (T2) by anthropometric
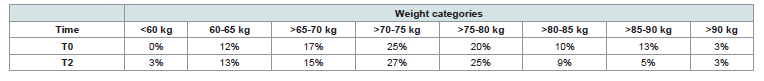
assessors.a. Body weight:
Participants’ weight was collected using an electronic scale [Table 2].
Table 1:Self-assessment ratings of cellulite parameters throughout the study and after 1-month follow-up. Calculation of the rate of improvement vs. baseline.
By comparing initial and final data, it was possible to calculate the
weight loss of each individual.
After two months, 80% of women experienced weight loss, with an average of 2.3 kg. Although the overall weight distribution of the cohort remained comparable, a slight shift toward lower weight categories was observed, particularly among women initially in higher weight ranges, suggesting a beneficial redistribution. Nearly 40% of participants lost more than 2 kg, supporting a moderate yet consistent effect on body weight regulation [Table 3].
After two months, 80% of women experienced weight loss, with an average of 2.3 kg. Although the overall weight distribution of the cohort remained comparable, a slight shift toward lower weight categories was observed, particularly among women initially in higher weight ranges, suggesting a beneficial redistribution. Nearly 40% of participants lost more than 2 kg, supporting a moderate yet consistent effect on body weight regulation [Table 3].
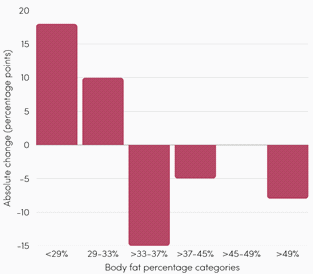
b. Body fat index:
Body fat percentage, another key indicator in cellulite assessment,
was measured using a fat caliper. After two months, 88% of
participants lost body fat, with an average decrease of 12.4%. The
proportion of women with a body fat percentage above 49% dropped
fivefold, while those with levels below 29% increased from 7% to 25%,
indicating a favorable rebalancing of body composition [Figure 1].
According to the American Council on Exercise, a healthy body fat
percentage for women is between 13% and 31%. At the start of the
study, approximately 22% of participants were in this range. After two
months of taking the nutricosmetic formula, this proportion reached
nearly 50%, demonstrating its positive impact on body composition
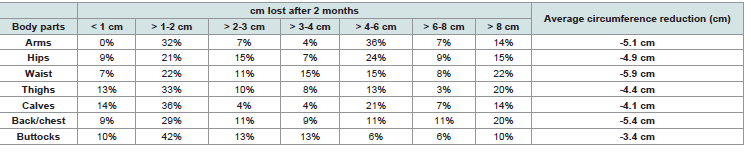
and helping women to achieve a healthy body fat amount [18].c. Body circumference:
Finally, circumference measurements showed that 98% of
participants had reduced at least one body area affected by cellulite
(waist, hips, thighs, arms, calves, back/chest, or buttocks). The most
marked decreases were observed at the waist (-5.9 cm), hips (-4.9
cm), and thighs (-4.4 cm) [Table 4] . These consistent reductions in
peripheral measurements suggest an overall improvement in tissue
tone and water distribution.Altogether, the objective findings align with the self-assessed improvements, supporting a concordance between perceived and measurable outcomes following two months of supplementation.
Discussion
This real-world study provides new evidence that daily
supplementation with Celluvine™, a patented nutricosmetic
combining grape extract and coenzyme Q10, improves multiple
parameters related to cellulite. After two months of supplementation,
women reported significant improvements in orange-peel appearance,
water retention, and self-perceived body image. These subjective
improvements were supported by objective reductions in body weight
(-2.3 kg on average), body fat (-12.4% on average), and circumferences
of cellulite-prone areas, particularly the waist (-5.9 cm), hips (-4.9
cm), and thighs (-4.4 cm), suggesting a multidimensional benefit on
both skin appearance and body composition.
These outcomes are consistent with data in the literature on bioactive compounds derived from grapes and other antioxidantbased nutricosmetics. In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Parandoosh et al. reported that supplementation with 300 mg/day of grape seed extract for 12 weeks significantly reduced body weight (-3.9 kg), waist circumference (-4.4 cm), and hip circumference
These outcomes are consistent with data in the literature on bioactive compounds derived from grapes and other antioxidantbased nutricosmetics. In a randomized, placebo-controlled trial, Parandoosh et al. reported that supplementation with 300 mg/day of grape seed extract for 12 weeks significantly reduced body weight (-3.9 kg), waist circumference (-4.4 cm), and hip circumference
Table 2:Distribution of participants according to their weight category at baseline and after 2 months.
Table 3:Distribution of participants who lost weight according to the number of kilograms lost after 2 months.
Table 4:Distribution of women according to the reduction in body circumference experienced after 2 months.
(-3.5 cm) in overweight adults, compared to baseline values [19].
Participants in the placebo group also showed a decrease in weight
(-1.9 kg), waist circumference (-1.2 cm), and hip circumference (-1.2
cm), probably due to the low-calorie diet associated with the study.
However, the more marked reductions observed in the supplemented
group suggest an additional physiological role for the polyphenols in
grape seed extract, linked to its antioxidant activity.
As a complex rich in polyphenols, grape seed extract has powerful
antioxidant activity capable of limiting adipocyte hypertrophy, as
demonstrated in vivo [20,21].
In this study, a similar reduction in waist and hip circumference was observed, suggesting that the grape-derived polyphenols contained in Celluvine™ may contribute to visible improvements in skin surface and body shape. The participants did not follow a lowcalorie diet, which reinforces the hypothesis that the changes observed are mainly related to the physiological effects of the formula’s active compounds on adipogenesis, lipolysis, and microcirculation, rather than to a change in lifestyle.
Compared with existing nutricosmetic data, the effects observed with Celluvine™ are consistent with those reported for other clinically validated anti-cellulite formulas. For example, Lemaire et al. showed that daily supplementation with 40 mg of SOD B Dimpless®, a superoxide dismutase extract from melon with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, resulted in a visible reduction in cellulite on the thighs of -6.8% after 56 days in a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study [22]. Although the assessment methods differ between studies, the conclusions are consistent. Oral nutricosmetic supplementation containing antioxidants, which can also modulate inflammatory pathways, appears to visibly improve the appearance of cellulite.
However, this study under real-life conditions has several limitations that should be acknowledged, including the small sample size, absence of a placebo group, and lack of dietary standardization, which may introduce variability. Future investigations should involve larger, more diverse populations, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, and advanced assessment methods such as laser Doppler imaging to clarify underlying mechanisms.
In this study, a similar reduction in waist and hip circumference was observed, suggesting that the grape-derived polyphenols contained in Celluvine™ may contribute to visible improvements in skin surface and body shape. The participants did not follow a lowcalorie diet, which reinforces the hypothesis that the changes observed are mainly related to the physiological effects of the formula’s active compounds on adipogenesis, lipolysis, and microcirculation, rather than to a change in lifestyle.
Compared with existing nutricosmetic data, the effects observed with Celluvine™ are consistent with those reported for other clinically validated anti-cellulite formulas. For example, Lemaire et al. showed that daily supplementation with 40 mg of SOD B Dimpless®, a superoxide dismutase extract from melon with strong antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, resulted in a visible reduction in cellulite on the thighs of -6.8% after 56 days in a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled study [22]. Although the assessment methods differ between studies, the conclusions are consistent. Oral nutricosmetic supplementation containing antioxidants, which can also modulate inflammatory pathways, appears to visibly improve the appearance of cellulite.
However, this study under real-life conditions has several limitations that should be acknowledged, including the small sample size, absence of a placebo group, and lack of dietary standardization, which may introduce variability. Future investigations should involve larger, more diverse populations, randomized, placebo-controlled trials, and advanced assessment methods such as laser Doppler imaging to clarify underlying mechanisms.
Conclusion
These results support the relevance of a targeted, multifactorial
nutricosmetic approach in cellulite management. By improving
microcirculatory function, modulating adipose tissue, supporting
collagen synthesis, and reducing oxidative stress, Celluvine™ has
been associated with measurable improvements in both subjective
and objective cellulite-related parameters and provides both visible
aesthetic benefits and improvements in physical comfort and
psychological well-being, with effects that appear sustainable beyond
the supplementation period.
The significant improvements observed in both subjective perceptions and objective measures suggest that the formulation may influence not only the appearance of the skin but also deeper physiological processes such as tissue oxygenation, lipid mobilization, and extracellular matrix integrity. The consistency of these effects across multiple endpoints, combined with the absence
The significant improvements observed in both subjective perceptions and objective measures suggest that the formulation may influence not only the appearance of the skin but also deeper physiological processes such as tissue oxygenation, lipid mobilization, and extracellular matrix integrity. The consistency of these effects across multiple endpoints, combined with the absence
of adverse events and a high level of compliance, underscores the
safety, tolerability, and consumer acceptability of this nutricosmetic
solution.
Beyond aesthetic enhancement, the reported improvements in physical comfort, sensation of lightness, and self-confidence further support the holistic value of Celluvine™ in promoting overall wellbeing. Taken together, these results strengthen the growing body of evidence supporting the use of natural bioactive ingredients as effective, non-invasive, and scientifically substantiated tools in beauty-from within strategies. Future placebo-controlled clinical studies integrating imaging, vascular, and biochemical assessment will help confirm these outcomes and further elucidate the synergistic mechanisms through which Celluvine™ contributes to long-term improvement in skin quality and body contour.
Beyond aesthetic enhancement, the reported improvements in physical comfort, sensation of lightness, and self-confidence further support the holistic value of Celluvine™ in promoting overall wellbeing. Taken together, these results strengthen the growing body of evidence supporting the use of natural bioactive ingredients as effective, non-invasive, and scientifically substantiated tools in beauty-from within strategies. Future placebo-controlled clinical studies integrating imaging, vascular, and biochemical assessment will help confirm these outcomes and further elucidate the synergistic mechanisms through which Celluvine™ contributes to long-term improvement in skin quality and body contour.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Expansion Consulteam for supervision
and coordination of the study, as well as the participants for their
time and cooperation.
Funding:This study was funded by Activ’Inside (Beychac-et- Caillau, France), the developer of the Celluvine™ nutricosmetic formulation. The sponsor provided the study material and covered operational costs but had no role in data collection, statistical analysis or interpretation of the results.
Conflicts of interest:All authors are full-time employees of Activ’Inside, the company that developed the product tested in this study. This affiliation did not influence the objectivity of the research or the interpretation of the results.
Ethics approval and consent to participate:This interventional study was based on the voluntary use of a food supplement for two months. Our consumer study did not require approval from an institutional ethics committee, as it involved no medical intervention, biological sampling, collection of sensitive personal data, or medical procedure. However, the study was conducted in accordance with internationally recognized ethical principles for research involving human participants, as outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, and followed good practices guidelines for market and consumer research (ICC/ESOMAR International Code). All participants were of legal age and provided written informed consent prior to their inclusion. Their participation was entirely voluntary, with the option to withdraw at any time, without any pressure.
Availability of data and materials:All relevant data supporting the conclusions of this study are presented in this article. Authors’ contributions: E.A. and I.G. contributed to the development of the study protocol, supervised the study, performed data analysis and interpretation, and were involved in manuscript writing. M.J., B.L., and D.G. also participated in manuscript writing, contributed to its critical revision, and approved the final version for publication.
Funding:This study was funded by Activ’Inside (Beychac-et- Caillau, France), the developer of the Celluvine™ nutricosmetic formulation. The sponsor provided the study material and covered operational costs but had no role in data collection, statistical analysis or interpretation of the results.
Conflicts of interest:All authors are full-time employees of Activ’Inside, the company that developed the product tested in this study. This affiliation did not influence the objectivity of the research or the interpretation of the results.
Ethics approval and consent to participate:This interventional study was based on the voluntary use of a food supplement for two months. Our consumer study did not require approval from an institutional ethics committee, as it involved no medical intervention, biological sampling, collection of sensitive personal data, or medical procedure. However, the study was conducted in accordance with internationally recognized ethical principles for research involving human participants, as outlined in the Declaration of Helsinki, and followed good practices guidelines for market and consumer research (ICC/ESOMAR International Code). All participants were of legal age and provided written informed consent prior to their inclusion. Their participation was entirely voluntary, with the option to withdraw at any time, without any pressure.
Availability of data and materials:All relevant data supporting the conclusions of this study are presented in this article. Authors’ contributions: E.A. and I.G. contributed to the development of the study protocol, supervised the study, performed data analysis and interpretation, and were involved in manuscript writing. M.J., B.L., and D.G. also participated in manuscript writing, contributed to its critical revision, and approved the final version for publication.