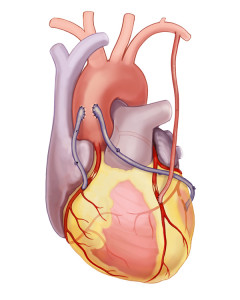
Coronary artery bypass surgery is commonly called as heart bypass surgery. Bypass surgery is a procedure that involves diverting of left internal thoracic artery to the left anterior descending branch of the left main coronary artery for the purpose of retaining normal blood flow. It is expected to relieve dysfunctioning of left ventricle and decrease the risk of death. though, it doesn’t prevent heart attacks. This surgery is performed usually heart being stopped, cardiopulmonary bypass takes up the role of heart during this period. However, this can be done even without the help of cardiopulmonary bypass or with the partial support of cardiopulmonary bypass.
Bypass is generally performed for the bypassing of arteriosclerosis, atherosclerosis or both. Arteriosclerosis is usually caused by thickening, loss of elasticity and calcification of arterial walls, which is leading to the narrowing of coronary artery, Cholesterol, lipids and cellular debris are being responsible for narrowing of arteries they often get clogged in the inner lining of coronary artery. Number of arteries can be bypassed, Single bypass, double bypass, triple bypass, quadruple bypass and quintuple bypass indicates the number of coronary arteries bypassed.
Medical uses
Bypass is usually performed on patients with defects in left main coronary artery, reduced or absent blood flow in multiple arteries that supply the heart etc.
Benefits
- Bypass surgery gives relief of angina when the blockage in arteries prevents the blood flow.
- Bypass surgery improves patient’s health with high risk of heart diseases. Gradually as the years pass the survival rate diminishes.
Precautions
- To prevent heart attacks, patient must exercise, give up on smoking, control on diet, maintain blood pressure under control.
- Decrease in cholesterol levels would prevent in blood clotting.
- Maintaining good health and medication is the only solution for avoiding vascular related loss.
- Holding a pillow against chest would help in quick healing of sternum.
- Avoid Coughing, laughing, sneezing, and blowing nose as these activities bring force against intra-thoracic and interrupt the healing process.
- Avoid using your hands assistance for sitting and standing.
- Avoid using pectoral muscle for raising objects.
- Avoid using arms overhead.
- Avoid sitting in car front seat.
Drawbacks
- Blood loss is observed in patient with surgery.
- Failure to take precautions can lead to delay in healing.