Journal of Addiction & Prevention
Download PDF
Research Article
*Address for Correspondence Saeid Rahmani, Kermanshah University of medical sciences, Kermanshah, Iran, Tel: +9354880565; E-mail: s.rahmani@gmail.com
Citation: Nooripour R, Rahmani S, Tavalaei SA, Alikhani M, Hosseinian S. Effectiveness of Psychodrama on Aggression of Female Addicts with Bipolar Personality. J Addiction Prevention. 2016;4(1): 4.
Copyright © 2016 Nooripour R, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Addiction & Prevention | ISSN: 2330-2178 | Volume: 4, Issue: 1
Submission: 10 February, 2016 | Accepted: 08 April, 2016 | Published: 12 April, 2016
Effectiveness of Psychodrama on Aggression of Female Addicts with Bipolar Personality
Roghieh Nooripour1, Gholam Ali Afrooz2, Saeid Rahmani3* Simin Hosseinian1, Seyed Abbas Tavalaei4 and Mostafa Alikhani5
- 1Department of Counseling, Faculty of Education & Psychology, Alzahra University, Tehran, Iran
- 2Department of Psychology, School of Psychology, TehranUniversity, Tehran, Iran
- 3Kermanshah University of Medical Sciences, Kermanshah, Iran
- 4Behavioural Sciences Research Centre, University of Medical Sciences Baqiyatallah, Tehran, Iran
- 5Department of Psychology, Substance Abuse Prevention Research Center, Kermanshah University of medical sciences, Kermanshah, Iran
*Address for Correspondence Saeid Rahmani, Kermanshah University of medical sciences, Kermanshah, Iran, Tel: +9354880565; E-mail: s.rahmani@gmail.com
Citation: Nooripour R, Rahmani S, Tavalaei SA, Alikhani M, Hosseinian S. Effectiveness of Psychodrama on Aggression of Female Addicts with Bipolar Personality. J Addiction Prevention. 2016;4(1): 4.
Copyright © 2016 Nooripour R, et al. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Journal of Addiction & Prevention | ISSN: 2330-2178 | Volume: 4, Issue: 1
Submission: 10 February, 2016 | Accepted: 08 April, 2016 | Published: 12 April, 2016
Abstract
Introduction: Mental disorders are a common problem in the world. Psychiatric disorders are the most aggressive. The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of psychodrama on aggression of female addicts with bipolar personality.Methods: This study is interventional study was conducted on 30 patients with bipolar personality. Patients were assigned to two groups randomly (n = 15). The aggression was estimated for each group. Then an experimental group psychodrama program but control group did not receive any treatment. After effectiveness, aggression scores of groups were compared.
Results: The mean score of aggression in the pre-test and post-test in the experimental group was significantly higher (P < 0.05). Covariance analysis showed that aggression score in the experimental group was significantly lower than the control group.
Conclusion: Results indicate positive effect of psychodrama on reducing aggression.
Keywords
Psychodrama; Aggression; Personality; Bipolar; AddictedIntroduction
Patients with borderline personality disorder, borderline between neurosis and psychosis are in vines and with great instability in affect, mood, behavior determined. A person with borderline personality disorder may consider the position of “most loved and the most important” in a position, as mentioned in the individual. Apparently there is equilibrium point in “the most brutal and the most exploitive person” from person as living [1].Skeptical, to compensate for flawed and confused identities often include words like mother on her skin, love or photos (like popular person or animal) are tattoo. This tattoo is relaxing in the ruling power. On the other hand these patients sensational and unstable relationships (sometimes associated with sexual carelessness) are involved. The important point of painful self-harm boundary repeated measures (the woman). They may help relieve tension or to different parts of inside body. But often in the arms, chest and “scarify or burn” of other measures to avoid real or imagined abandonment; “crazy” can be seen abdomen. The pattern of unstable and intense interpersonal relationships characterized by swings between two poles, and worthless idealization of, or behaviors “gesture” makes clear, continued instability and self-evident; impulsive behavior; repeatedly threatened suicide or self-injury behavior, emotional instability due to the reactive nature of creation, intense anger or difficulty controlling anger or thinking disproportionate temporary stress-related paranoia or severe dissociative symptoms typical symptoms of this disorder [2].
Mental disorders are one of common problems that many people have faced it. According to the World Health Organization in 2001 about 45 million people worldwide suffer from mental disorders [3]. Various studies shows the prevalence of mental disorders in different countries have reported between 7-40% [4,5].
Surveys in fourteen countries showed that anxiety disorders and mood disorders as the most common psychological disorders were discussed [6]. Other common psychological disorders can be pointed to aggression. In various studies the prevalence of aggression 5 to 20 percent [7,8].
Aggressive behavior in addition to the adverse effects of on interpersonal communication also has adverse effects on internal states and mental well-being. Untreated aggression can lead to problems of interpersonal or internal symptoms such as physical illness, migraine headaches [9]. There are different methods for treating mental disorders such as: drug therapy, cognitive therapy, group therapy, etc. can be mentioned. Studies have shown that the use of methods such as music therapy, art therapy, drama therapy, film and dance therapy can be effective in the treatment of psychiatric disorders [10]. The effect of so much drama therapy is widely accepted that in some of the world’s leading hospitals for treatment of his mental illness in general. In view of the monitor to achieve goals of medical treatment, getting rid of stress and physical and mental harmony and personal growth are used [11].
Although accurate and reliable statistics on the prevalence of mental disorders in Iran does not exist, but studies shows that the prevalence of mental disorders in Iran is lower than in other countries, based on various studies carried out 12 to 43 percent of the population is involved [12,13]. Recognition and proper use of the therapy in patients with these disorders is very important. This study was aimed to investigate the effect of radio plays in the treatment of patients suffering from aggression planned and executed. The aim of this study is to investigate the effectiveness of psychodrama on aggression female addicts with bipolar personality.
Methods
This study is an interventional study on a random sample of 30 addicts with bipolar personality. Among 22 to 55-year-old female patient admitted in Tehran were selected and randomly divided into control and experimental groups.Patients who fulfilled the DSM-V-TR criteria for substance (opium) dependence (by smoking or oral intake) were enrolled as opium dependent patients. Meanwhile, the data from patients’ coronary angiography report were also added to our data.
Participants were administered modified version of the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-V (SCID) and the Structured Interview for DSM-V Personality (SIDP-IV) [14,15]. Diagnostic raters were highly trained, mostly Ph.D. clinical psychologists and monitored throughout the project to minimize rater drift.
Those patients have below criteria:
•Instability in interpersonal relationships, self-image and emotional state, as well as obviously being impulsive
• With a flurry of anxious efforts to avoid real or imagined abandonment
• loss of interest in activities once enjoyed, including sex• Unstable and severe unstable identity
• Impulsivity in at least two areas of areas of potential harm to an individual (e.g. spending, sex, substance abuse)
• thinking of death or suicide, or attempting suicide• Instability in the People’s emotional state as revealed reactivity
• Chronic feelings of emptiness
• Inappropriate, intense anger or difficulty in mastering the anger of
• The incidence of paranoid thoughts
Personality deviation scale for aggression
This instrument is Likert scale questionnaire of 36 questions. This is edition of aggression scale questionnaire and guidance. This questionnaire has three subscales that they are hostile to evaluate thoughts and actions and include cross-disciplinary, consisting of 6 questions to evaluate lack of confidence and 6 questions to evaluate the excessive dependence on others that both of them had at least one vision Critical indicate. 6 questions to evaluate the attitudes of social hegemony and domination are 6 questions to evaluate the antagonistic or not inhibited [16]. Reliability and validity of questionnaire studied in Iran and on the appropriate [17].
In the next stage personality deviation scale distributed among the groups and they were asked to complete questionnaires on what they feel at the time of their completion, the show was broadcast. To realize the attention of participants to view, and double identification with the characters, 4 written questions on the subject of display, distributed before the second series of questionnaires were distributed and explained to the patients themselves rather than the character, and to respond to essay questions, after the implementation of psychodrama, again the questionnaires were distributed. In the control group personality deviation scale distribution and they were asked to complete the questionnaire. Then for 20 minutes for this group was shown a television program and again after the patients were asked to answer questions. Aggression scores in both groups before and after the performances were evaluated and compared. Before the tests was necessary coordination with the doctor for each patient. It is also no secret the information about each patient in the study were fully considered.
Analyzed data by using paired t-test to compare the groups in the pre-test and analysis of covariance for the elimination of the pre-test to compare two groups of SPSS 19 software was used in this study. All tests are two-tailed significance level was set at less than 0.05.
Results
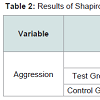
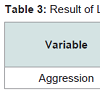
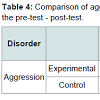
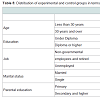
Covariance analysis was used to evaluate data normality and covariance and homogeneity of pretest scores between the two groups.In order to examine the normality data, the Shapiro Wilk test was used. The Levine test was used to evaluate homogeneity of variance within groups. According to the data in Tables 1-3, the findings were not significant (α = 0.05 level). Assumptions were inferred about normality and homogeneity of data covariance and regression slope, and the use of covariance were permitted for evaluation of assumptions with homogeneity of covariance. According to aggression scores in the experimental group was significantly decreased after training while the second phase (control group) was increased (Tables 4 and 5). Totally, 15 patients in the experimental group and 15 patients in the control group were analyzed. Significant differences between the two groups in terms of age, marital status, occupation and education level there (P < 0.05), the educational level of the experimental group was significantly higher than the control group (P < 0.05).
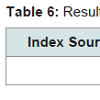
According to Table 6, the results shows significance (α = 0.05), and therefore it can be concluded that psychodrama was effective in aggression of female addicts with bipolar personality.
Discussion and Conclusion
The results of this study showed that treatment of mental disorders such as aggression psychodrama can be effective. Perhaps the reason for this effect explains that the show treated like any other psychotherapy tries to change feelings and perceptions, attitudes and behaviors that have created a kind of exit disorder to help him. The psychodrama has a special place. Psychodrama that can recognize imaginative sense of hearing presentations will be conducted with higher cognitive and rational. Significant changes in thinking and rational knowledge is able to provide treatment and psychological balance.As stated earlier the process of random selection, try to be consistent in the group as much as possible and it was observed that the experimental and control groups in terms of age, occupation, education level are almost identical. Of course, in terms of education, there are differences between the two groups and education groups than the control, but using covariance analysis the effect of such distortion is eliminated pointers.
The results of this study showed that the results of this study showed that the treatment of mental disorders such as aggression psychodrama can be effective. Perhaps the reason for this effect explains that the show treated like any other psychotherapy tries to change the feelings and perceptions, attitudes and behaviors that have created an individual exit disorder to help him. Among these are special places. Psychodrama and imaginative effects by taking full advantage of word and music, and to create opportunities, can understand the sense of hearing presentations will be conducted with higher cognitive and rational. Significant changes in thinking and rational knowledge is able to provide treatment and psychological balance.
As stated earlier the random selection process, we tried to be consistent in the group as much as possible and it was observed that the experimental and control groups in terms of age, occupation, education level are almost identical. Of course, in terms of education, there are differences between the two groups and education groups than the control, but using covariance analysis the effect of such distortion is eliminated pointers.
However, as this study has been done in Iran and even other parts of the world, but the results of this study with similar studies conducted on the impact of drama therapy on improvement of psychiatric disorders as well. For example, in a review article in 2007 emphasized the effective role of drama therapy for schizophrenia [18]. In study conducted by Molavi and his colleagues determined that increasing social skills and self-esteem drama therapy is effective in patients with schizophrenia [19]. As well as drama therapy was effective in reducing aggression in educable mental retardation [11]. Fakhri and colleagues showed that drama therapy can improve motor skills and auditory memory of people with mental retardation [20]. The limitations of this study include the limited intervention and follow-up meetings in the next time and the inability to control all the factors mentioned. The small number of subjects from a teaching hospital, and limitations in the choice of subjects with different gender and other factors that are difficult to generalize the results of virtually, therefore interpretation of the results to be careful.
The aggression is reduced, while the mean score of the control group increased aggression in the post. Since intervention in the control group were not applied, the increased aggression scores in the control group test we can say that perhaps the problem could be related to waiting time control group. As for this group was neutral program and according to the psychological state of the participants and the patience they often did not show high interest to tolerate waiting time.
In summary, it can be concluded that the use of psychodrama can be a useful therapy in treating patients with mental disorders, although perhaps not possible using this method alone and as complement to other treatment methods used. Multicenter study using a larger sample size and composition of different gender and also by taking all factors in the recovery process of patients as well as studies to evaluate the effectiveness compared to other treatments is recommended.
References
- Perugi G, Fornaro M, Akiskal H (2011) Are atypical depression, borderline personality disorder and bipolar II disorder overlapping manifestations of a common cyclothymic diathesis? World Psychiatry 10: 45-51.
- Elisei S, Anastasi S, Verdolini N (2012) The continuum between bipolar disorder and borderline personality disorder. Psychiatr Danub 24 Suppl 1: S143-S146.
- Ahmadvand A, Sepehrmanesh Z, Ghoreyshi FS, Assarian F, Moosavi GA, et al. (2010) Prevalence of mental disorders in general population of Kashan city. Iran J Epidemiol 6: 16-24.
- Kosiyakul J (2008) Epidemiology of psychiatric disorder in Priest Hospital in 2003-2007. J Med Assoc Thai 91 (Suppl 1): S37-S40.
- Sankaranarayanan J, Puumala SE (2007) Epidemiology and characteristics of emergency departments visits by US adults with psychiatric disorder and antipsychotic mention from 2000 to 2004. Curr Med Res Opin 23: 1375-1385.
- (2000) Cross-national comparisons of prevalence and correlates of mental disorders. WHO International Consortium in Psychiatric Epidemiology. Bull World Health Organ 78: 413-426.
- Chukwujekwu DC, Stanley PC (2011) Prevalence and correlates of aggression among psychiatric in-patients at Jos University Teaching Hospital. Niger J Clin Pract 14: 163-167.
- Gale C, Arroll B, Coverdale J (2009) The 12-month prevalence of patient-initiated aggression against psychiatrists: a New Zealand national survey. Int J Psychiatry Med 39: 79-87.
- Sadeghi A, Ahmadi SA, Abedi MR (2002) A study of the effectiveness of group trainings in anger managementin a rational emotional behavioral style. J Psychol 6: 52-62.
- Soltani HR, Alahyari AA, Rasoulzade Tabatabayi SK, Soltani N (2011) The effect of musical themes on reduction of aggression in university students. Ofogh-e-Danesh 16: 34-39.
- Hashemi M, Mirzamani MS, Davarmanesh A, Salehi M, Nezadi-Kashani G (2011) The effect of puppetry (with UV light) in reduction of aggression of educable mental retarded female students. J Rehabil 11: 88-93.
- Chegini S, Nikpour B, Bagheri Yazdi SA (2002) Epidemiology of mental disorders in Qom, 2000. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 4: 44-51.
- Mohammadi MR, Rahgozar M, Bagheri Yazdi SA, Mesgarpour B, et al. (2005) An epidemiological study of psychological disorders in Chaharmahal & Bakhtiari province, 2001. Shahrekord University Of Medical Sciences Journal 6: 33-42.
- First M, Spitzer R, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (1996) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis I disorders - patient edition (SCID-I/P, version 2.0). New York: Biometrics Research Department, New York State Psychiatric Institute, pp. 56-75.
- Pfohl N, Blum, M, Zimmerman B (1997) Structured interview for DSM-IV personality. American Psychiatric Press Inc, Washington, D.C.
- Deary IJ, Bedford A, Fowkes FG (1995) The Personality deviance scales: their development, associations, factor structure and restructuring. Pers Individ Dif 19: 275-291.
- Mahmoodi GR (2000) Evaluation of validity and reliability of Personality Deviance Scale. Tehran: Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch
- Ruddy R, Dent-Brown K (2007) Drama therapy for schizophrenia or schizophrenia-like illnesses. Cochrane database of systematic reviews: CD005378.
- Molavi P, Ghamari-Givi H, Rajabi S, Berahmand O, Rasool-zadeh B, et al. (2009) Psychordrama effect on social skills and self esteem of schizophrenic patient. J Rehabil 10: 68-73.
- Fakhri F, Aghaei H, Khajehhosseini H (2005) Surveying the effectiveness of the drama therapy on increasing of motor skills and the hearing memory of the persons with mentally disabled with an I.Q of 55-70. J Rehabil: 24-28.